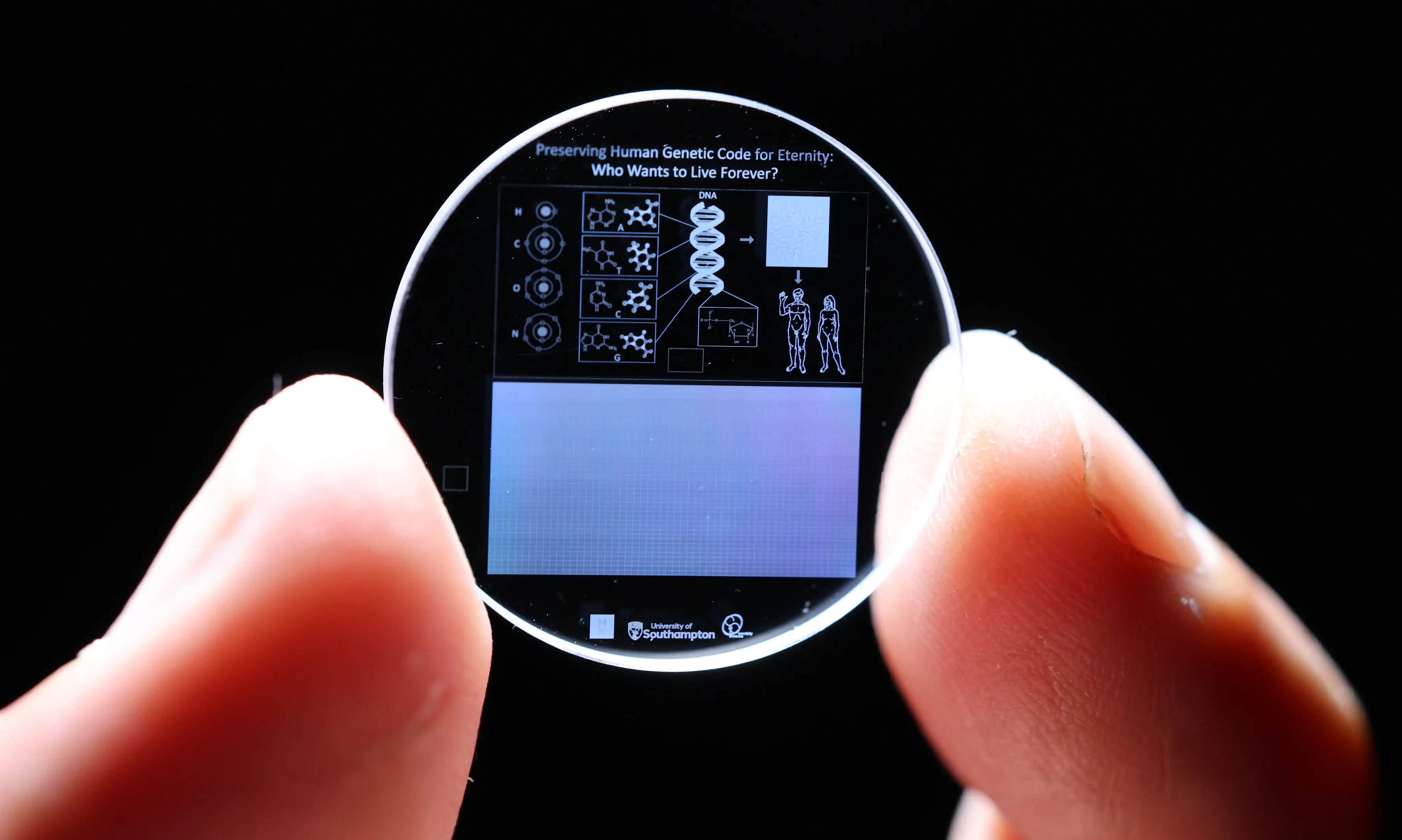
Researchers at the University of Southampton in the UK successfully stored the entirety of the human genome sequence onto an indestructible 5D optical memory crystal no bigger than a penny. The indestructibility claims are no joke since the discs can withstand temperatures up to 1,000°C, cosmic radiation, and even direct impact forces of 10 tons per cm2.


Went to the article seeking answers but got only more questions.
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/5D_optical_data_storage
☹️
/edit
Further down in the article it is a little clearer…
The website even lists a little more…
So, it’s supposedly three dimensions of position plus angle and (maybe?) polarity. So, it seems to be more than just a marketing gimmick, but I can’t find any information about the resolution of those additional two parameters, so I can’t tell if a single voxel stores two bits or two terabits.
It sounds kinda like the “trick” on the internet for fitting more notes onto a note-sheet for an exam. You’re still using the same physical space to store information, but you’re introducing a new degree of freedom that allows you to increase storage density.
Seems more like 5 axis than 5 dimensions.
Sounds like a slice through the crystal that can be moved up and down and rotated through 2 angles (eg roll and pitch)
5 axis and 5 dimensions are essentially the same thing, right? A 2D graph has 2 axes, a 3D one has three, 4D graph can be shown with colour representing the 4th axis, etc.
Yeh, axis was the wrong term. I was thinking degrees of freedom.
However, I misunderstood the concept.
The extra dimensions are basically optical manipulation, like the other comment says with the red and blue lenses.
I thought it was more about the crystals attitude. So in addition to x, y and z, you also have alpha, beta, gamma.
Which would be 3 dimensions/axis with 6 degrees of freedom
So, as I understand it, and I don’t, 5D is just fancy marketing due to the really weird properties of the crystals used to store the data in. They are just calling properties of the crystal, dimensions.
I found the wiki page on it https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/5D_optical_data_storage
According to the University of Southampton:
It’s actually cromulent technical terminology to call those extra degrees of freedom “dimensions”, it’s only in common parlance that “dimension” is restricted specifically to spatial dimension. Having hundreds or even thousands of dimensions is not unknown in data science.
The extra dimensions are time and inception. I now know less about it than when I started.